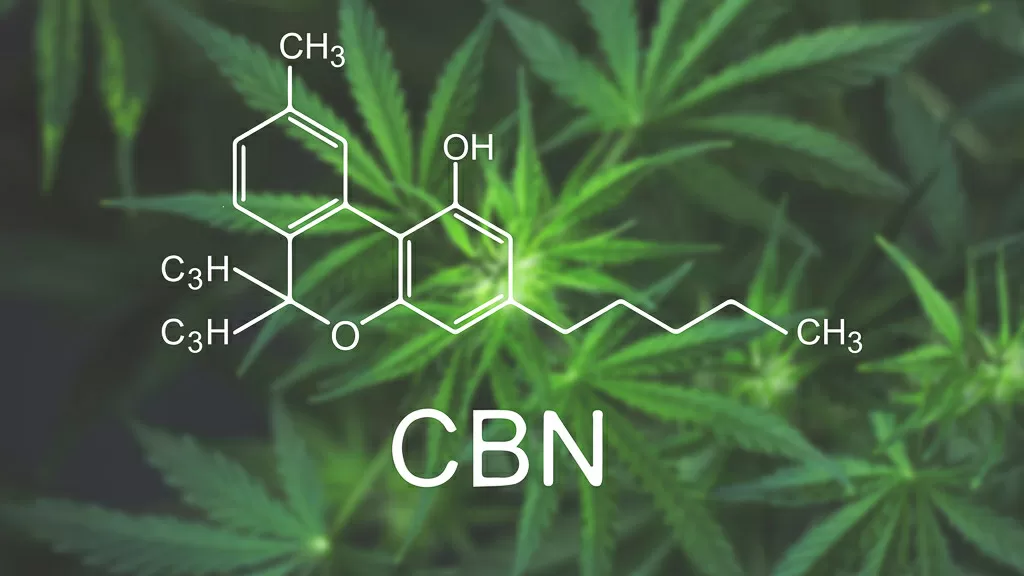
Generally speaking, when talking about the compounds and active ingredients commonly found in cannabis, THC and CBD are undoubtedly the most frequently mentioned.
However, it is the more than 80 cannabinoids that determine the composition of sativa hemp, including CBN or cannabinol, which is becoming increasingly well known, especially in view of the numerous studies examining its medical and scientific applications and effects.
Its concentration in cannabis inflorescences does not exceed 1% and it is precisely CBN that tends to represent a sort of side-effect of excessive 'maturation' or drying of the weed: it is in fact the direct consequence of the degradation of THC due to direct exposure to sources of heat or oxygen that favour its oxidative processes, inevitably compromising the quality of the plant material.
What is Cannabinol
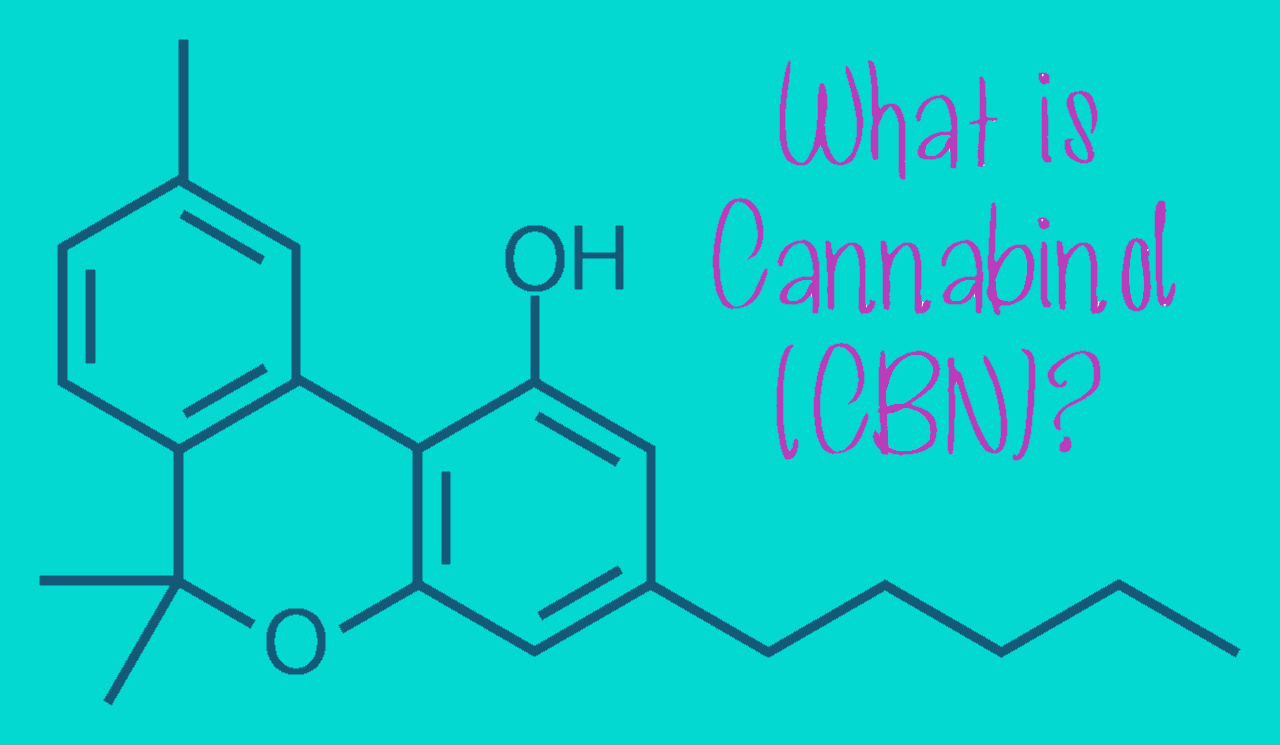
Cannabis comprises more than 80 different cannabinoids, each of which plays its own role in determining the typical benefits associated with the weed plant. THC (tetracannabidiol) and CBD (cannabidiol) are undoubtedly the most well-known: the former is the active compound par excellence present in hydroponic ganja, which determines the characteristic psychotropic and psychoactive effects of the herb, while the latter is directly responsible for the main therapeutic actions applied mainly in the medical field.
However, THC and CBD are not the only ones: for years now, CBN or cannabinol has also been the subject of scientific research and studies due to its characteristic sedative effects.
It was the first cannabinoid to be isolated, even ahead of THC: the discovery of its chemical structure, composed of 21 carbon atoms, 26 hydrogen atoms and 2 oxygen atoms, dates back to the 1940s by Dr Roger Adams, although it was not until 1963 that the molecule was isolated, when Raphael Mechoulam began to prove its therapeutic benefits through controlled laboratory tests.
Initially thought to be responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis, CBN only took a back seat following the discovery of THC: it became the subject of study again with the advent of global legalisation and legal marijuana.
Although closely related to pure THC, it has no psychoactive effects: unlike other cannabinoids, CBN does not come directly from the plant but is the result of an actual oxidation process of the tetracannabidiol, the same process that occurs when cannabis is dried and stored for a long period of time. It has proven to have strong calming and relaxing effects, making it at least similar to CBD, especially when taken in combination with THC.
Although it acts as a weak agonist at CB1 receptors in the brain, it has a greater affinity for CB2 receptors in immune cells, and because of its selectivity as a CB2 receptor agonist it is mainly used as an immunosuppressant.
This means that, although cannabinol does not have the ability to bind to cannabinoid receptors, it does have a potent, predominantly sedative effect: numerous studies have shown that 5mg CBN is as effective as 10mg Diazepam or alternative pharmaceuticals with similar sedative properties.
Main effects of Cannabinol
Although CBN has sedative properties, it is not psychoactive, making it a particularly interesting object when evaluated from a therapeutic point of view. However, the CBN content commonly found in cannabis is decidedly low, rarely exceeding a concentration of 1% per dried inflorescence.
This factor does not, however, affect the body's response to the active ingredient: several studies have shown in recent years that cannabinol stimulates the growth of bone tissue by indirectly recruiting a very small number of mesenchymal stem cells directly from the surrounding bone marrow, a feature which in future could make the active ingredient extremely effective in the treatment and regeneration of bone fractures.
Studies and scientific research have shown that cannabinol is responsible for a markedly relaxing action that can significantly improve sleep quality. Combined with various terpenes, CBN also has analgesic, anticonvulsant and anxiolytic properties, and although medical interest in cannabinol has always been limited compared to the better-known cannabinoids THC and CBD, research now suggests that it could also be a powerful antibacterial agent against particularly persistent strains of bacteria such as MRSA, which are typically resistant to traditional antibiotics.
CBN may also be a powerful neuroprotectant. In a study with rodents, researchers used CBN as a treatment for ALS and found that it delayed the onset of ALS. Although studies in humans have yet to be conducted, this factor could reveal the effectiveness of cannabinol in treating degenerative diseases.
Further research carried out in the same way on laboratory rats revealed that CBN gradually increased the amount of food eaten by the rodents, leading to speculation that it was also effective in stimulating appetite. Since patients suffering from eating disorders often fear taking THC, which is responsible for the so-called 'munchies', because of its euphoric effects, CBN could potentially offer a viable alternative for treating loss of appetite due to HIV, AIDS, anorexia, bulimia or simple lack of appetite.
CBN may also be useful in the treatment of glaucoma. A study carried out on rabbits has shown that cannabinol, like THC, can reduce intraocular pressure, the main risk factor for glaucoma. However, this research is still in its embryonic stage and has not so far revealed that the active ingredient is more effective than conventional drugs used to treat glaucoma.
Only further research will therefore be able to show whether cannabinoids are really able to effectively replace all kinds of treatments covered by conventional medicine. Last, but certainly not least, CBN could prove decisive in the treatment of diseases of the osteoarticular system such as rheumatoid arthritis, thanks to its typical anti-inflammatory action.
Although this has yet to be demonstrated, it is plausible to argue that the multiple potentialities of cannabinol could in the future support the treatment of various more or less disabling diseases, effectively assisting the now well-known action of CBD.
Differences between Cbn, Cbd and Thc
Cannabinoids have different chemical properties and equally different effects, depending on dosage, susceptibility and the way cannabis is taken. Commonly found in cannabis sativa plants, a wide range of active ingredients, including THC, CBD and CBN, can be taken in general when taking medical marijuana.
However, each active ingredient can be extracted and isolated, as well as produced in synthetic form in order to exploit its individual properties, without exposing the body to the full range, a factor that can usually lead to some scepticism among occasional weed users, due to the dreaded manifestations of the substance's high.
Each cannabinoid has distinct characteristics, the main one being tetracannabidiol THC, a psychoactive substance that can significantly affect brain function and mental state, temporarily altering mood, perception and behaviour. The many different strains of cannabis available have different concentrations of THC, which in turn produce different psychoactive effects. However, the active ingredient itself is generally used to treat conditions such as nausea, poor appetite, glaucoma and pain manifestations.
Unlike THC, cannabidiol (cbd) has no psychoactive effects and does not alter mental state, behaviour or perception in any way. It has a calming and relaxing effect, which is why it is now widely used to treat anxiety, depression, panic and insomnia, as well as being an effective and increasingly popular pain therapy.
CBD or cannabinol, on the other hand, still generates numerous doubts about its possible psychoactive effects: some studies mention that it has no action, others describe it as mild, and although it seems to have potentially powerful sedative effects, we are still a long way from defining its real potential.
Is Cannabinol psychoactive?
Is cannabinol or CBN considered psychoactive? The answer is uncertain, since all the research conducted to date on the active ingredient has been carried out on mice or laboratory rats, and has therefore not been conclusive with regard to the human organism. It would therefore be only slightly intoxicating in the proportion of ¼ of THC in terms of potency, a cannabinoid from which it derives thanks to the relative degradation promoted by exposing the drying marijuana buds to oxygen and heat for a long time.
 Italiano
Italiano Español
Español English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch